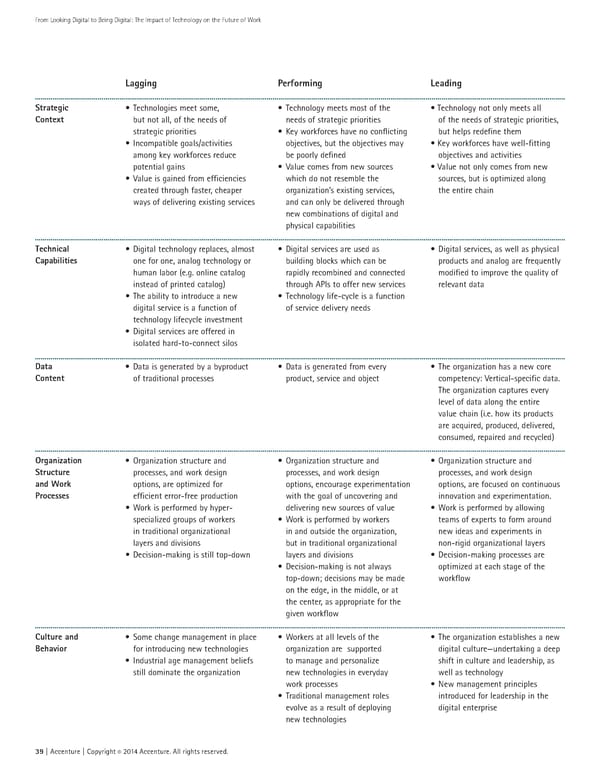
From Looking Digital to Being Digital: The Impact of Technology on the Future of Work Lagging Performing Leading Strategic • Technologies meet some, • Technology meets most of the • Technology not only meets all Context but not all, of the needs of needs of strategic priorities of the needs of strategic priorities, strategic priorities • Key workforces have no conflicting but helps redefine them • Incompatible goals/activities objectives, but the objectives may • Key workforces have well-fitting among key workforces reduce be poorly defined objectives and activities potential gains • Value comes from new sources • Value not only comes from new • Value is gained from efficiencies which do not resemble the sources, but is optimized along created through faster, cheaper organization’s existing services, the entire chain ways of delivering existing services and can only be delivered through new combinations of digital and physical capabilities Technical • Digital technology replaces, almost • Digital services are used as • Digital services, as well as physical Capabilities one for one, analog technology or building blocks which can be products and analog are frequently human labor (e.g. online catalog rapidly recombined and connected modified to improve the quality of instead of printed catalog) through APIs to offer new services relevant data • The ability to introduce a new • Technology life-cycle is a function digital service is a function of of service delivery needs technology lifecycle investment • Digital services are offered in isolated hard-to-connect silos Data • Data is generated by a byproduct • Data is generated from every • The organization has a new core Content of traditional processes product, service and object competency: Vertical-specific data. The organization captures every level of data along the entire value chain (i.e. how its products are acquired, produced, delivered, consumed, repaired and recycled) Organization • Organization structure and • Organization structure and • Organization structure and Structure processes, and work design processes, and work design processes, and work design and Work options, are optimized for options, encourage experimentation options, are focused on continuous Processes efficient error-free production with the goal of uncovering and innovation and experimentation. • Work is performed by hyper- delivering new sources of value • Work is performed by allowing specialized groups of workers • Work is performed by workers teams of experts to form around in traditional organizational in and outside the organization, new ideas and experiments in layers and divisions but in traditional organizational non-rigid organizational layers • Decision-making is still top-down layers and divisions • Decision-making processes are • Decision-making is not always optimized at each stage of the top-down; decisions may be made workflow on the edge, in the middle, or at the center, as appropriate for the given workflow Culture and • Some change management in place • Workers at all levels of the • The organization establishes a new Behavior for introducing new technologies organization are supported digital culture—undertaking a deep • Industrial age management beliefs to manage and personalize shift in culture and leadership, as still dominate the organization new technologies in everyday well as technology work processes • New management principles • Traditional management roles introduced for leadership in the evolve as a result of deploying digital enterprise new technologies 39 | Accenture | Copyright 2014 Accenture. All rights reserved. ©
 From Looking Digital to Being Digital Page 37 Page 39
From Looking Digital to Being Digital Page 37 Page 39