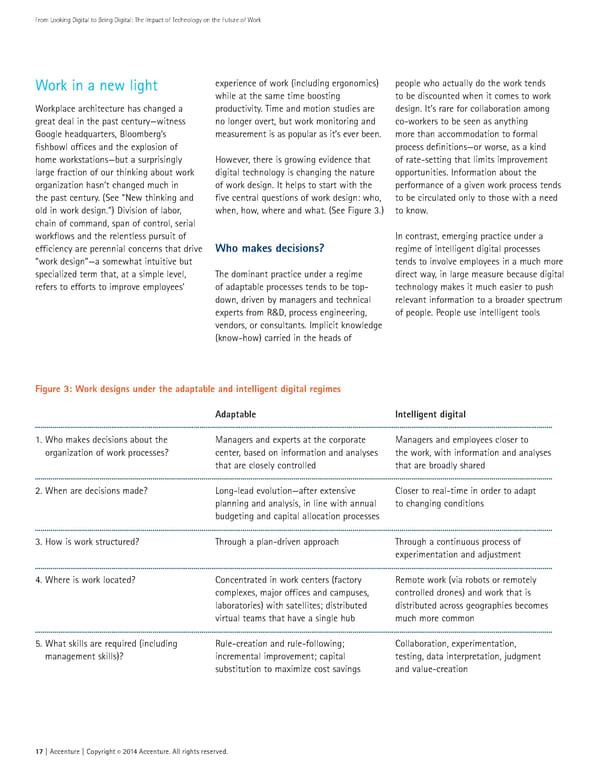
From Looking Digital to Being Digital: The Impact of Technology on the Future of Work Work in a new light experience of work (including ergonomics) people who actually do the work tends while at the same time boosting to be discounted when it comes to work Workplace architecture has changed a productivity. Time and motion studies are design. It’s rare for collaboration among great deal in the past century—witness no longer overt, but work monitoring and co-workers to be seen as anything Google headquarters, Bloomberg’s measurement is as popular as it’s ever been. more than accommodation to formal fishbowl offices and the explosion of process definitions—or worse, as a kind home workstations—but a surprisingly However, there is growing evidence that of rate-setting that limits improvement large fraction of our thinking about work digital technology is changing the nature opportunities. Information about the organization hasn’t changed much in of work design. It helps to start with the performance of a given work process tends the past century. (See “New thinking and five central questions of work design: who, to be circulated only to those with a need old in work design.”) Division of labor, when, how, where and what. (See Figure 3.) to know. chain of command, span of control, serial workflows and the relentless pursuit of In contrast, emerging practice under a efficiency are perennial concerns that drive Who makes decisions? regime of intelligent digital processes “work design”—a somewhat intuitive but tends to involve employees in a much more specialized term that, at a simple level, The dominant practice under a regime direct way, in large measure because digital refers to efforts to improve employees’ of adaptable processes tends to be top- technology makes it much easier to push down, driven by managers and technical relevant information to a broader spectrum experts from R&D, process engineering, of people. People use intelligent tools vendors, or consultants. Implicit knowledge (know-how) carried in the heads of Figure 3: Work designs under the adaptable and intelligent digital regimes Adaptable Intelligent digital 1. Who makes decisions about the Managers and experts at the corporate Managers and employees closer to organization of work processes? center, based on information and analyses the work, with information and analyses that are closely controlled that are broadly shared 2. When are decisions made? Long-lead evolution—after extensive Closer to real-time in order to adapt planning and analysis, in line with annual to changing conditions budgeting and capital allocation processes 3. How is work structured? Through a plan-driven approach Through a continuous process of experimentation and adjustment 4. Where is work located? Concentrated in work centers (factory Remote work (via robots or remotely complexes, major offices and campuses, controlled drones) and work that is laboratories) with satellites; distributed distributed across geographies becomes virtual teams that have a single hub much more common 5. What skills are required (including Rule-creation and rule-following; Collaboration, experimentation, management skills)? incremental improvement; capital testing, data interpretation, judgment substitution to maximize cost savings and value-creation 17 | Accenture | Copyright 2014 Accenture. All rights reserved. ©
 From Looking Digital to Being Digital Page 15 Page 17
From Looking Digital to Being Digital Page 15 Page 17